This is truly one of the largest collections of atomic structure worksheets in one place. These worksheets have students explore the nature of atoms and their structure. We look at the function of each of the subatomic particles and how they interact to form molecules and ions. We break down the anatomy of these structures to display this for students and we will explore the Bohr model of this structure. Students will learn how to predict the element formed based on the number of protons an atom has. We will look at how mass number affects the balance of the atom. We will also look at how electrons are positioned and concept of orbital diagrams and how to determine valence shell configurations and what this means about the nature of the atom. Students will learn how to display valence shells with Lewis Dot diagrams. We will advance on to looking further into the nucleus and explore nuclear chemistry of atoms that are not very stable. We will also look at how this affects an atoms location on the Periodic Table of Elements. We first help students identify the basic parts and then work on how electron configuration affects the chemical nature of substances.
Print Atomic Structure Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.

Atoms and Molecules
Basic facts to get us started. An example question would be: Which of the following terms refers to the smallest part of a compound that has all the properties of that compound?
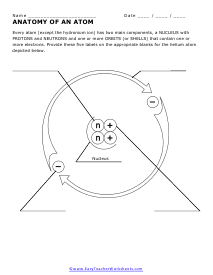
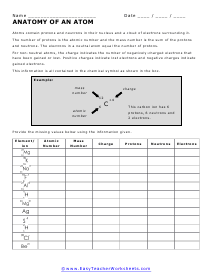
Anatomy of an Atom
We peek into the true anatomy of these buggers. Every atom (except the hydronium ion) has two main components, a NUCLEUS with PROTONS and NEUTRONS and one or more ORBITS (or SHELLS) that contain one or more electrons.
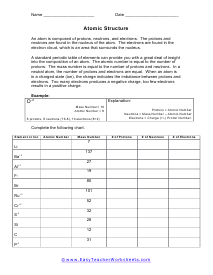
Atomic Numbers, Elements, and Ions
You are given an element or ion name and an atomic number. We ask you to tell us about what it composed of. An atom is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus. The electrons are found in the electron cloud, which is an area that surrounds the nucleus.

Atomic Structure Practice Sheet 1
Example problem: What is the mass number, symbol, and charge of an ion that contains 35 protons, 45 neutrons and 36 electrons?

Practice Sheet 2
We are looking for a wide range of data based on the information that is provided to you about an element or ion.
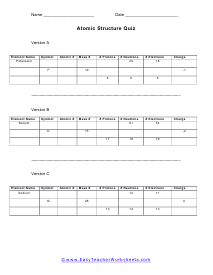
Atomic Structure Quiz
You will give 3 pieces of data and are asked to complete this here chart for us. The data given may include element name, symbol, atomic number, number of sub atomic-particles (protons, electrons, neutrons), and any charge that may exist.

Electron Configuration
Show us where the electrons are located. Write the complete electron configuration for each of the following elements.
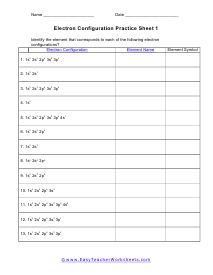
Electron Configuration Practice Sheet 1
Identify the element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations. It is stated in orbital notation.

Electron Orbital Diagrams
Draw orbital diagrams for the following choices. You will across note the directionals.

Electron Configuration Review Sheet
Given an element and a mass number you will tell us the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons. You will also diagram the electron configuration in an orbital diagram.

Valence Electrons
The electrons found in the outer most energy level are collectively referred to as valence electrons.

Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet
Lewis Dot Diagrams are used to indicate the number of valence electrons and provide us with a quick form of short hand.

Overall Review Worksheet
Given an element, like Magnesium (Atomic Number 12, Mass Number 24), please provide all the following information for this element.

Electron Configuration Quiz: Form A
For identified element identify the ground state electron configuration, orbital diagram, Lewis dot diagram, and number of valence.
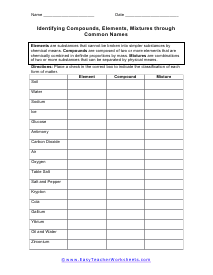
Identifying Compounds, Elements, Mixtures through Common Names
Place a check in the correct box to indicate the classification of each form of matter. All of the substances described uses common names that most people will recognize.
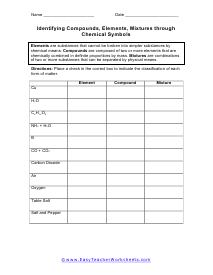
Chemical Symbols
You will be given chemical symbols for elements, compounds, or a mixture and asked to state the phase of matter you find this at room temperature.
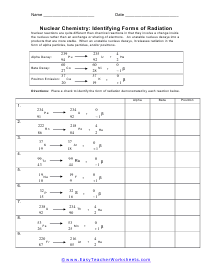
Nuclear Chemistry: Identifying Forms of Radiation
Place a check to identify the form of radiation demonstrated by each reaction below.

Predicting Nuclear Decay Products
Predict the products of the following nuclear reactions. You may need to balance a reaction or two.
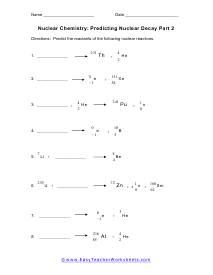
Predicting Nuclear Decay Reactants
What is going on with these nuclear reactions? What reactants were needed to create these products.

Half-life Worksheet
Radioactive substances decay at a constant rate. There are a number of unstable nuclei that decay in a given time. The time that it takes for half of the atoms in a given sample of an element to decay is termed the half-life.
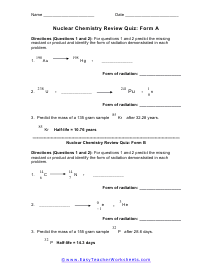
Nuclear Chemistry Review Quiz: Form A
For questions 1 and 2 predict the missing reactant or product and identify the form of radiation demonstrated in each problem.

Nuclear Chemistry Quiz Part 2
Write the electron configuration, orbital diagram, total number of valence electrons, and Lewis dot structure.

Nuclear Chemistry Quiz Part 3
This is the 3rd page of this quiz in this series. The questions center around naming elements, compounds, and mixtures. You will also balance nuclear reactions.


Unit Test: Form B
You will test your knowledge once again using all that you have learned. Identify the element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations.

Unit Test B: Page 2
This page tests your ability to write Lewis Dot diagrams and determine the total number of valence electrons.

Unit Test B: Page 3
This will test two skills: 1) Your ability to indicate if the item presented is an element, compound, or mixture. 2) Balancing chemical reactions and missing parts.

Unit Test B: Page 4 - Halflife
All the questions on this page are about determining the half life of substances.
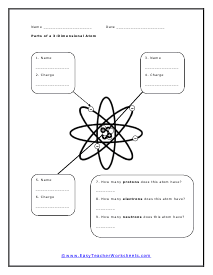
Parts of a 3-Dimensional Atom
This may look a bit different than others. Label all the parts and tell us what we know about this particular atom based on the sub-atomic particle arrangement.
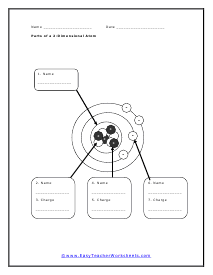
Parts of a 2-Dimensional Atom
Charge it all up. This is very similar to the last worksheet, but it is flat.
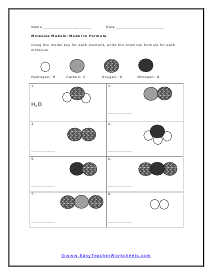
Model to Formula
Using the model key for each element, write the chemical formula for each molecule.
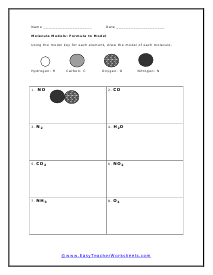
Formula to Model
We do the same thing as the last worksheet, but we go in the opposite direction. It is pretty cool how you can do that.
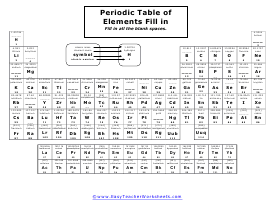
Periodic Table of Elements Fill In Worksheet
What is missing in here? Make sure to check the entire table. Use the legend and key to help you.
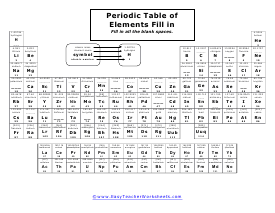
Periodic Table Fill in Part 2
Find those different elements and parts. Same as the last worksheet, but you will see some different missing parts
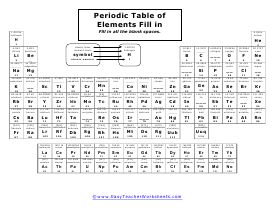
Missing Elements
The element you want to see is missing. Can you determine everything that is missing?
Composition of an Atom
The number of protons is the atomic number and the mass number is the sum of the protons and neutrons. The electrons in a neutral atom equal the number of protons. You will use this to complete this worksheet.

The Bohr Model
Bohr models (or Bohr diagram) are diagrams that show the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and the electrons in each electron energy level around it.

Atoms in a Molecule
Provide the number of atoms in each molecule of the substances represented by the chemical formulas below.
What Are Atoms and What is Their Significance?
An atom is one of the most significant things in the world as it is the smallest unit of matter. When one atom connects with another atom, they make up a chemical element. Atoms were initially thought to be the smallest particle of matter, but they are actually composed of three smaller particles.
The atom is the unit of matter that forms all elements in the universe. The parts of the atom are the proton, neutron, and electron. The protons and neutrons inhabit the atom’s nucleus (or center), while electrons spin around the outside of the nucleus. Every living thing is made of atoms.
Since atoms are part of all living and non-living things, they are crucial to scientific study. Read on to learn the three primary parts of an atom, the most common atoms, and how the Periodic Table identifies elements by the number of atoms.
What is An Atom?
The word "atom" is derived from a Greek word for "uncuttable". Atoms are thought to be the smallest particle of a single element. There are smaller parts of it, but the makeup and arrangement does determine the properties of an element. It is pretty cool because how we mix up atoms up or together can make just about anything in the universe. You find three simple sub-atomic particles in each atom. In the center (nucleus) you will find neutrons and protons. Together they provide almost all of the mass for the element. Protons have a positive charge and neutrons have no charge. Spinning around the nucleus you will find electrons. They have a negative charge and provide very little mass to the overall element.
Atoms are essential pieces of matter, with matter being anything you can physically touch. The only thing in the world not made of atoms is energy. Atoms can connect to form molecules, and molecules form all the physical world you see.
Atoms have three parts that work together. The protons carry a positive charge, while the electrons have a negative charge. The neutrons have no charge. All atoms have the same number of protons and electrons, and most atoms have the same number of protons and neutrons.
The significance of atoms is that without them, nothing could exist. They are the building blocks of all chemical structures. When atoms combine, they create individual compounds that are part of the universe.
The Four Most Common Atoms
The four most common atoms are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. In all, there are over one hundred discovered atoms. Let’s learn some interesting facts about these common atoms and how they impact the world around us.
- Hydrogen is the simplest element and comprises two of the same atoms. It is a colorless, weightless gas. Hydrogen is in water and comprises sixty-one percent of the human body’s atoms.
- Carbon atoms can link together to make some of the longest, most durable chains. Carbon can form limitless molecules that vary in size, composition, and shape. It is the only element with a field of chemistry focusing only on its compounds–organic chemistry.
- Oxygen is a tasteless, odorless gas that all living things need for breathing. Oxygen is the third most plentiful element, with hydrogen being the most abundant and helium being second.
- Nitrogen is the fourth most common atom, making up about seventy-five percent of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is also an odorless, tasteless, colorless gas and is the fifth most plentiful element in the universe.
The Relationship Between the Periodic Table And Atoms
The Periodic Table is a chart of chemical elements (made up of atoms) organized into rows where elements with a similar structure are grouped together. The name of the chart comes from the arrangement of the elements.
The rows from left to right are termed periods, while the rows from top to bottom are called groups. There are one hundred and eighteen elements on the table and scientists will add two more soon.
Why Atoms Have Atomic Numbers on the Periodic Table
The atoms in each unique element have a specific number of protons. For example, oxygen has two atoms so its atomic number is 2. Iron has twenty-six protons in its nucleus so the atomic number is 26. Scientists can identify an element by its atomic number on the chart.
Conclusion
Atoms, the tiniest unit of matter, make up all things. Considering that all living and non-living matter are made up of atoms, this is a significant concept to understand for scientific study.


