We often forget the importance of rocks and minerals in our daily lives. They form in nature and they are created three different ways. Igneous rock is formed when the Earth’s molten layers (magma) cools and forms a hard solid. Sedimentary rock takes time to form. As the layers of the Earth settle and form sediment, the rock layer forms. Metamorphic rock starts out as one of the other two and undergoes a great deal of heat and pressure. Whenever tectonic plates collide, you will find a bunch of metamorphic rock in its path. Below you will find worksheets that teach you how to create crystals, classify rocks, label soil layers, and identify the parts of the rock cycle. You with also learn to name the different types of rocks and how they are formed.
Print Rocks and Minerals Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.
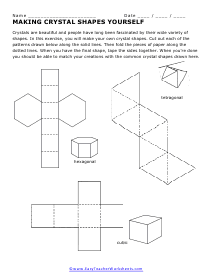
Making Crystals
Crystals are beautiful and people have long been fascinated by their wide variety of shapes. In this exercise, you will make your own crystal shapes.
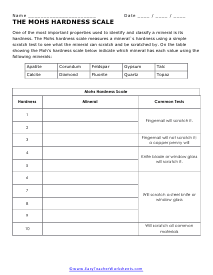
The Mohs Hardness Scale
One of the most important properties used to identify and classify a mineral is its hardness. The Mohs hardness scale measures a mineral's hardness using a simple scratch test to see what the mineral can scratch and be scratched by.
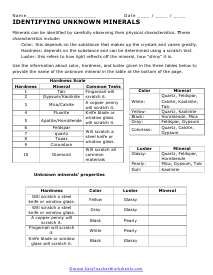
Unknown Minerals
Minerals can be identified by carefully observing their physical characteristics. You will use all of the descriptions to determine the type of mineral.
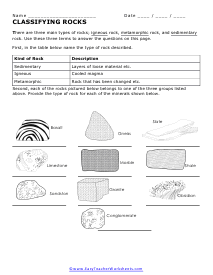
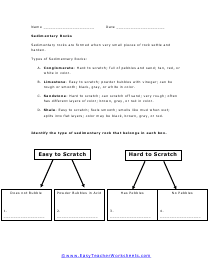
Classifying Rocks
There are three main types of rocks; igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Use these three terms to answer the questions on this page.


Soil Layers
Soil and earth can have several layers and each has different structures and organisms. Look at the diagram of a soil profile pictured below.
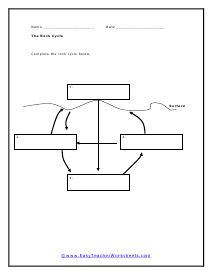
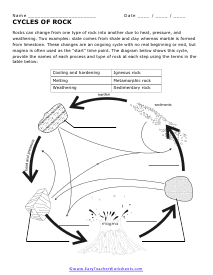
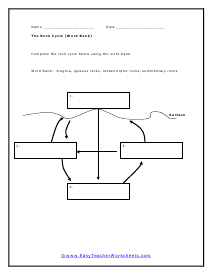
The Rock Cycle
Move those rocks around in one spot. This is the process that transforms rcoks from one form to another.
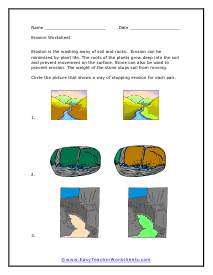
Erosion Worksheet
Erosion is the washing away of soil and rocks. Erosion can be minimized by plant life. The roots of the plants grow deep into the soil and prevent movement on the surface.
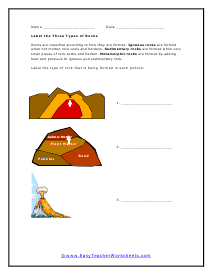
Label the Three Types of Rocks
Rocks are classified according to how they are formed. Igneous is formed when hot molten forms cools and hardens. Sedimentary rocks are formed when very small pieces of it settle and harden. Metamorphic types are formed by adding heat and pressure to igneous and sedimentary forms.


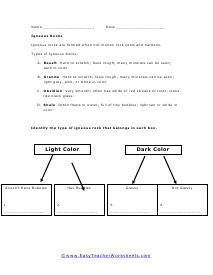

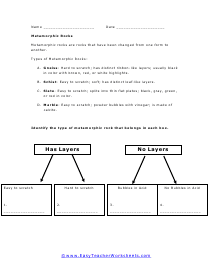
Metamorphic Rocks
Identify the type of metamorphic rock that belongs in each box. These are all formed under high levels of heat.

Rock Identification Activity
Choose 3 rocks from the provided collection. Make sure each it looks completely different.
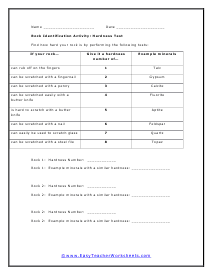
Rock Identification Activity: Hardness Test
Find how hard your rock is by performing the following tests.

Rock Identification Activity
Is this rock igneous, metamorphic, or sedimentary? Used what you have learned to determine this.


One More Try
You will have a series thoughts to better udnerstand what you are looking at. You will answer questions such as: Is the rock magnetic?

What Are the Different Types of Rocks and Minerals?
You see, the Earth is pretty awesome. From ordinary volcanic rocks like granite to priceless jewels used in jewelry, it is home to various rocks and minerals that are much more complicated than meets the eye.
The different types of rocks and minerals are sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. These rocks form under specific conditions such as melting, cooling, erosion, compaction, or deformation. On the other hand, minerals can be divided into metallic and non-metallic based on their composition.
How do we differentiate rocks and minerals, and how do we classify them? This article will help you discover the difference between a rock and a mineral and closely examine their various types.
Minerals vs. Rocks
A mineral is a substance with unique chemical and physical properties, composition, and structure, whereas a rock is a solid collection of various minerals.
Rocks are typically composed of two or more minerals combined through various geological processes. So, minerals are the building blocks of rocks.
The Different Types of Rocks
The three types of rock - sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic – are classified based on their physical properties, chemistry, and origin.
Igneous
Molten rock (lava or magma) crystallizes and hardens to produce igneous rocks. The melt starts below the Earth near hot areas or active plate borders before rising to the surface. Because heat transforms minerals into igneous rocks, these formations are usually very dense and shiny.
Sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are broken pieces of other rocks that have been worn down by erosion and weathering. As these small pieces find new homes in new places, they settle in and pack down to form a solid stone with many layers. These rocks often contain sand, silt, dead plants, and animal bones.
Metamorphic
Other types of rocks transform into metamorphic rocks due to high heat or pressure, or more typically, a combination of both.
Check out this article from the American Museum of Natural History to learn more about the three types of rocks and how they look.
How Rocks Are Formed: The Rock Cycle
Any rock may transform into any other type of rock, though this process typically takes a long time. Some transformations take place above or below the Earth's surface. The rock cycle refers to the sequence of natural processes transforming a rock.
Rock can change through three major processes:
- Cooling and Crystallization. The Earth's interior is hot enough to produce magma or gooey molten rock. As this magma makes its way back up to the earth’s crust, it cools, forming the crystalline structures that make up igneous rocks.
- Weathering and Erosion. Rocks erode over time as wind, ice, plants, and animals wear them down. These influences can eventually split rocks into sediment - which looks like dirt or sand. Then, glaciers, wind, and moving water move these bits from one place to another in a process called erosion.
- Sedimentation. At some point, the sediments are dropped or deposited. This process is called sedimentation. The sediments may then be pressed and cemented together, forming sedimentary rock.
- Metamorphism. Metamorphism is the transformation within a body of rock due to high pressure and high temperature. As pressure and temperature rise, new metamorphic rocks can form from old ones.
The Different Types of Minerals
Now that we know about the different types of rocks and the Rock Cycle let's learn about the different kinds of minerals.
Minerals are classified based on their crystal form and chemistry. They are divided into two types: metallic and non-metallic.
Metallic Minerals
Metallic minerals are minerals composed of at least one metal. These often occur as mineral deposits and are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. Iron, copper, gold, silver, etc., are some common metallic minerals.
Non-Metallic Minerals
Non-metallic minerals are those minerals that do not contain any metals. Diamonds, mica, salt, potash, clay, and dolomite are non-metallic minerals. Since these minerals don’t include metal, they are usually more brittle and breakable than metallic minerals.
Conclusion
There are three categories of rocks based on their origin and characteristics: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic, and two types of minerals based on their composition: metallic and non-metallic. However, there is still much to learn about rocks and minerals.
Going outside or looking at images of different rocks and minerals is the best way to learn more about this fascinating topic. Just take a second look at the rocks around you, and you’ll open your eyes to the incredible variety in the natural world!


