We look at the structure and function of plant parts, as well as the process that take place inside their organelles. This series of worksheets takes a deep dive into the plant kingdom. We start by looking at the structure and function of the main parts of the organisms. We take an inside look at leaves and what makes them tick. Then we dive to the bottom and take an inside look at a root and what allows it to suck in nutrients and continue to grow. We also look at flowers and how they spread pollen to allow a species to continue on for hundreds of years. As we move on students will read passages that explain many facets of plants and we will look at some weird ones too. Students will explore the concept of gas exchange and the carbon dioxide and oxygen cycles that provide the world will the needed compounds. We will finish of by looking at adaptations that wonderful organisms have made to thrive in their nearby environment.
Print Plants Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.
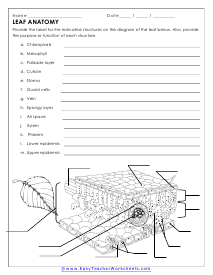
Leaf Anatomy
Provide the label for the indicated structures on the diagram of the leaf below. Also, provide the purpose or function of each structure.

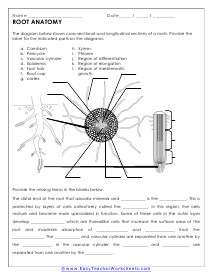
Root Anatomy
The diagram below shows cross-sectional and longitudinal sections of a roots. Provide the label for the indicated parts on the diagrams.

Flower Anatomy
Provide the label for the parts of the flower in the diagram below and give the purpose/function of each part.
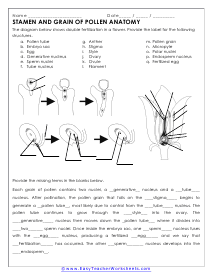
Anatomy of Pollen
The diagram below shows double fertilization in a flower. Provide the label for the following structures.

How Do Plants Grow?
Adult produce seeds that fall near them or get carried by wind, water, insects or animals to another location. Those seeds that land in a suitable spot will naturally enter into the soil and stay there until conditions are right for the seed to germinate, that is, begin to grow.


Short Answer Questions
People who work in nurseries grow plants from seed. Would you like to work in a nursery? Explain why or why not.

The Basic Structures
There are thousands of species of plants on Earth but in this lesson we will focus on the anatomy of the most abundant kinds, those that grow from seeds with their roots in the soil.

Anatomy Multiple Choice Questions
Above ground, branches may form along the main stem. Leaves will be found along the main stem if the plant does have any branches. Otherwise, leaves are on the branches.


How Do Plants Make Their Own Food?
Humans rely on plants for food. Even the meat we eat comes indirectly from them. For example, cattle are the source of the beef we eat and cattle graze on plant material.

Page 2 of Reading Passage
Photosynthesis combines water and carbon dioxide using energy from the sun to produce sugars as food for the plants. Photosynthesis also breaks down carbon dioxide and releases oxygen into the atmosphere for humans and animals to breathe.

Food Multiple Choice Questions
Remember that trees are plants and like other plants trees feed themselves through photosynthesis. Forests clean the air of the carbon dioxide and produce oxygen for all animals, including humans, to breathe. Forests are an important part of the earth's life cycle.

Food Short Answer Questions
To most people sugar is a granular white substance. Is this the sugar that plants produce during photosynthesis? If you don't know the answer, look it up.

How Plants Reproduce
There are hundreds of thousands of plant species that grow in all kinds of conditions everywhere in the world. With such a great diversity, it's easy to understand that they have several different types of reproduction but all plants of the same species use the same method of reproduction.

How Plants Flower
Flowering plants create seeds from their flowers through sexual reproduction. Flowering plants have male and female parts inside the flower.

Flowering Multiple Choice Questions
There are tens of thousands of plant species that don't have flowers. They use asexual reproduction to create new babies that are clones of the parent.

Flowering Short Answer Questions
The largest clump of aspen trees, called Pando, is located in the state of Utah. Do some research and write a short report about Pando.

Strange Plants
The plants that we are accustomed to seeing every day have roots in the soil; have a center stalk or, in the case of trees, a trunk; and obtain their food through photosynthesis.

Strange Plants Page 2
There are even plants that don't require any soil for growth. Some aquatic plants like the water hyacinth live by floating in water with roots that dangle downward.

Strange Multiple Choice Questions
The most famous plants that are in the strange category are carnivorous. They obtain some of their nutrients by trapping and digesting insects and sometimes small amphibians like little frogs.

Strange Ones Short Answer Questions
Write a short story about a dragonfly that avoids being captured by a Venus flytrap plant. Look up the natural habitat of the Venus flytrap in the Carolinas and use factual details of the surroundings in your story.

Basic Structure of Plant Cells
The bodies of all living things are made up of cells. The smallest living things are composed of just one cell. Bacteria and some algae are examples of one-celled living things but bacteria are neither plants nor animals.
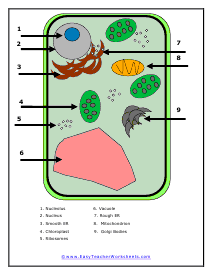
Plant Cell Color Diagram
A very clear diagram to print in color. With all of the cell organelles labeled.

Basic Structure of Plant Cells Multiple Choice Questions
What plant structure acts as a storage tank for water and nutrients?

Basic Structure of Plant Cells Short Answer Questions
What is the difference between the cell wall and the cell membrane of plant cells?

Pollinators
Flowering plants reproduce sexually which means they have a male part called the stamen and a female part called the pistil.

Pollinators Multiple Choice Questions
What part of a plant produces pollen? We look at questions such as that.

Pollinators Short Answer Questions
Often part of a springtime weather report is the pollen count for people who have allergies. Explain what the pollen count is.

Plants and Oxygen
Animals, including humans, require a constant supply of oxygen for breathing. Without sufficient oxygen an animal suffocates and dies.
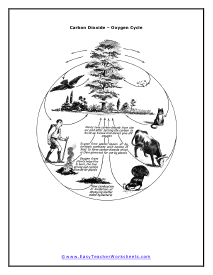
Carbon Dioxide - Oxygen Cycle
It shows the movement of both substances. The process of photosynthesis produces oxygen as a waste product. Carbon Dioxide is also used during this process.

Oxygen Questions
Exactly how does this process of converting carbon dioxide to oxygen work? First of all it is a chemical process that occurs inside the plant.

Oxygen Short Answer Questions
Scientists are concerned about having too much carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide emissions from cars. Explain one reason why you think they are concerned.

Adaptations
The natural world is a fascinating place. There are hundreds of thousands of unique plant and animal species that have adapted to living in every type of biome and niche in the world.

Adaptations Multiple Choice Questions
Most plants need soil nutrients, sunlight and moisture in order to survive yet many have adapted to living in the dry and often extremely hot desert biome.

Adaptations Short Answer Questions
Lichens are adapted to life all across North America from warm areas to the arctic tundra. Do some research and explain why lichens are not plants.

Creating Your Own Garden
One of the first steps in creating a garden is to decide what to plant there. Some are annuals that grow from seed each year.

Creating Your Own Garden Multiple Choice Questions
Another important consideration in gardening is where to put the garden spot. Remember that most plants, especially flowers and vegetables, need sunshine and moisture.

Creating Your Own Garden Short Answer Questions
Locate pictures of 15 different vegetables and create a poster of these pictures. Identify each vegetable and list why it is healthy to humans.
What Are the Plant Parts and Their Functions?
Plants are responsible for providing energy either directly or indirectly for most of the planet. Plants are unique in that they are one of the few organisms that can make their own food. As long as they have access to oxygen and water they are good to go. Some plants are carnivorous and can eat small bugs or in some cases even small frogs. Others like Bamboo can grow crazy fast. In the right conditions Bamboo has been known to grow almost a meter in just a day. Collectively the rainforests supply the planet with half of its oxygen supply. Did you know that an Apple is a quarter air and Cabbage is over ninety-percent water.
Plants are impressive organisms - they produce their own food, endure all kinds of weather, and come in various types. A plant's parts make all of these remarkable capabilities possible.
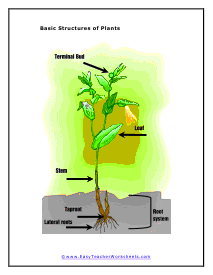
Essential plant parts include the roots, stems, and leaves. These parts produce food, transport water and nutrients, and enable plant growth and development. Roots absorb nutrients and water, which leaves use to make food. Stems transport resources between roots, leaves, and other parts.
I'll discuss a few plant parts and their functions throughout this article. Keep reading to understand how they all work together.
What Are Roots and Their Functions?
Roots are the plant parts that absorb water and nutrients from the soil and transport them to other parts. They also serve as a plant's anchor. Aside from that, they can also serve as storage for photosynthetic products.
Some roots that act as storage are bulbous roots, which store starch.
Understanding Different Roots Systems
All of a plant's roots work together as a system. There are two kinds of root systems:
Tap roots. These roots grow vertically as one main root, with few small root branches or lateral roots. An example of a plant with tap roots is a carrot.
Fibrous roots. These roots tend to have a lot of lateral roots so that they can extend horizontally. Thus, they appear dense, which helps them prevent erosion. Examples of fibrous roots are bananas and grass.
While we may typically think of roots as the stringy plant parts below the soil surface, not all root systems are like that.
Mangroves, for instance, have aerial or stilted roots that may be exposed to air or water but aren't buried in the soil.
What Are Stems and Their Functions?
Stems help compose a plant's shoot system and provide structural support. The shoot system also helps transport nutrients and water from the roots to farther parts, like leaves. They also transport products to storage sites. Modified shoots can store photosynthetic products.
Stems can vary in thickness, length, and appearance. They can be tough and woody or soft and herbaceous. While they're typically seen above the surface, some plants, like potatoes, have them underground.
Essential Components of the Stem
These are the parts of the stem:
Nodes. These are points on the stem to which other plant parts, like leaves or flowers, attach.
Internodes. These are the stem segments that connect one node to the next.
What Are Leaves and Their Functions?
Leaves are components of shoot systems, and their prominent role is to photosynthesize. Photosynthesis is the production of food from sunlight and water. They collect sunlight using chlorophyll and get water delivered by stems from the roots.
Leaves Enable Photosynthesis in Plants
Photosynthesis is a process unique to most autotrophic organisms or those that can produce their own food.
A single equation can sum up the process of photosynthesis:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
This equation means that six parts of carbon dioxide (CO2), six parts of water (H2O), and sunlight are used by leaves to produce 1 part of sugar (C6H12O6) and six parts of oxygen (O2).
Why Are Most Leaves Green?
Most leaves are green because of the presence of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a pigment that helps capture energy from sunlight for food production or photosynthesis. However, some pigments can mask it, which explains why some leaves aren't green in color.
Other pigments present in plants include the following:
Carotenoids. These produce yellow to orange colors, such as the color of carrots. Leaves during the fall season turn yellow to orange because only carotenoids are left.
Anthocyanins. These produce pink to red hues, such as the color of apples. Leaves that are red during the fall primarily have anthocyanin in them instead of carotenoids.
Final Thoughts
Leaves, roots, and stems are essential parts of a plant. They are crucial for survival, development, resource collection, and food production. Most of them are present in plants, in one way or another. However, they may appear differently in other plants or are absent if not needed.


