This selection of worksheets covers all the major aspects of school-based chemistry. We begin by comparing the organic compounds to compounds that do and do not include carbon. We explore chemical reactions that require water and produce it as a byproduct. Students will learn the differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. We look at chemical symbols and formulas for them as well. We at the concept of exothermic and endothermic reactions and how that results during phase changes. This is one of our bigger science sections. The sheets found here start with organic chemistry and advance to understanding the interactions between substances including energy release and bonding.
Print Chemistry Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.

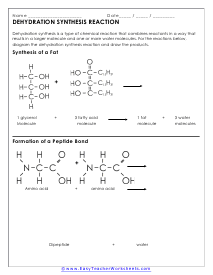
The Dehydration Sythesis Reaction
Dehydration synthesis is a type of chemical reaction that combines reactants in a way that results in a larger molecule and one or more water molecules.
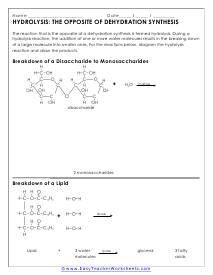
The Hydrolysis Reaction
The reaction that is the opposite of a dehydration synthesis is termed hydrolysis. During a hydrolysis reaction, the addition of one or more water molecules results in the breaking down of a large molecule into smaller ones.

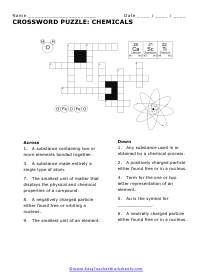
Chemical Symbols Crossword
Use the symbols to find the names of the elements needed to complete the puzzle.
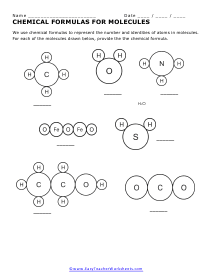
Formulas of Molecules
We use chemical formulas to represent the number and identities of atoms in molecules. For each of the molecules drawn below, provide the chemical formula.
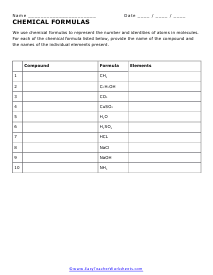
Compound and Elements
We use chemical formulas to represent the number and identities of atoms in molecules. For each of the chemical formula listed below, provide the name of the compound and the names of the individual elements present.

Heat Energy
Joules and calories are the units used to measure heat energy. When heat is emitted or absorbed, the amount of heat transferred is calculated via the following formula.

Phase Changes and Heat Exchange
During a phase change heat energy is absorbed or emitted to change the phase of the material, but the temperature remains the same

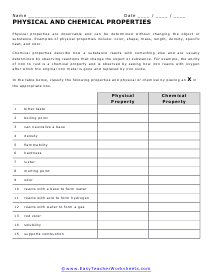
Mixture or Substance?
In the table below, classify the following materials as substances or mixtures by writing S or M respectively in the empty boxes.


Colloids, Solutions, and Suspensions
Label the following liquid mixtures as a solution, colloid or suspension and provide an example of each type of mixture.
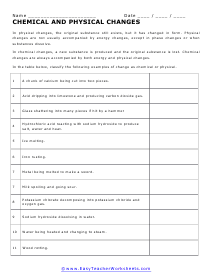
Chemical and Physical Changes
In the table below, classify the following examples of change as chemical or physical.

Separating Mixtures
Often we wish to separate mixtures into their individual components (e.g., if one is more valuable or useful on its own) We can do this by using the differences in the physical and chemical properties of the components.



Properties of Metals and Nonmetals
We give you a property and you tell us if it's for metals or nonmetals.

Element Activity
Keeping these properties in mind and by using a periodic table, indicate the most chemically active element in each pair.

Types of Chemical Bonds
Describe the bond between the elements as covalent (nonmetal and metal), ionic (nonmetal and metal), or both (for compounds containing a polyatomic ion).

The Conservation of Mass
Mass is not gained nor lost during chemical reactions; atoms are merely rearranged into different compounds. The total mass of the reactants in a chemical process is therefore equal to the total mass of the products.

Mass Relationships in Equations
We can use a balanced chemical equation and the molecular weights to determine the mass relationships involved in a chemical reaction.
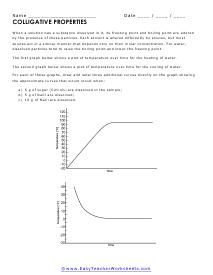
Colligative Properties of Substances
When a solution has a substance dissolved in it, its freezing point and boiling point are altered by the presence of these particles.

Calculating Mass and Volume
Use the mass/volume concentration concept, provide the answers to the questions.

Calculating Percentage By Volume Concentrations
Several different concentrations of solutes in solvents are used in practice. One of these is the % by volume concentration which is calculated via the equation shown in the box.

Calculating Percentage By Mass Concentrations
Several different concentrations of solutes in solvents are used in practice. One of these is the % by mass concentration which is calculated via the equation shown in the box.

Solubility of Compounds
Follow the general rules for solubility and provide labels indicating whether the following compounds are soluble or insoluble.

Radioactive Decay Rates
A half-life is the time required for one-half of a radioactive material to decay and change to another element.
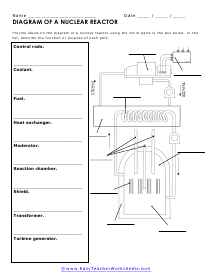
Diagraming Nuclear Reactors
Provide labels on the diagram of a nuclear reactor using the list of parts in the box below. In the list, describe the function or purpose of each part.

Alternative Fuel Crossword
Some interesting answers can be found here. We look at natural gas, hydrogen, propane, oils, and electricity.
What Is Chemistry?
When we want to understand the world and all the processes that happen within it, we turn to chemistry.
Chemistry is a branch of study that deals with matter. It covers matter's components, properties, natural laws, processes, and transformations. This study has its branches and concentrations.
In modern times we often do not realize how often chemistry affects our lives. We use shampoo and conditioner to keep our hair soft and manageable. We then brush our teeth with whitening tooth paste and rinse with anti-plaque mouthwash. Chemists formulated all those substances for you without you even realizing it. Chemistry affects you before you are even awake for your day. This is the branch of science that studies matter and interactions between substances. This science is used in all walks of life from the moment you wake up and brush your teeth to the moment you answer your mobile phone. It is a very math intensive science. You will learn things like the most common element in the universe is hydrogen. You will also learn that the most used controlled reaction is fire. It is used to make more things and mostly like the pinnacle tool used by humans.
What Are the Branches of Chemistry?
Nearly everything on earth is a form of matter. Since chemistry studies matter, its scope is extensive. Thus, it makes sense for the study to be divided into branches.
Chemistry has five main branches, including physical, organic and inorganic, analytical, and biochemistry. While these branches can stand by themselves, they often interact with each other.
- Physical. Physical chemistry deals with the principles that govern atoms, molecules, reactions, and chemical systems. Some specific concepts it tackles are reaction rates, energy transfers, molecular structures, the interaction of light and matter, and thermodynamics.
- Organic. Organic chemistry is the branch that deals with carbon-containing compounds. Carbon and other elements like nitrogen and oxygen form the building blocks of life and essential substances like medicines.
- Inorganic. The study of compounds that don't contain carbon is inorganic chemistry. Inorganic chem has many applications because it deals with objects like minerals.
- Analytical. Analytical chemistry involves a lot of calculations and experiments because it is focused on quantifying substances. For instance, titration experiments are a familiar aspect of analytical chemistry.
- Biochemistry. The chemical processes and principles that underlie biological systems are explored in biochemistry.
As mentioned, these branches often interact with each other. For instance, biochemistry may need analytical or organic chemistry to understand specific biological reactions.
Other Concentrations of Chemistry
As we understand the world better, our knowledge expands. Such expansion gives rise to a new set of sub-disciplines in chemistry called concentrations.
There are many possible concentrations in chemistry, and here are a few of them:
- Nuclear. Nuclear chemistry investigates the reactions that happen within atoms. Some applications are power generation through nuclear plants and medicine through radioactive therapies.
- Polymer. Polymers are molecular chains with repeating subunits. The synthesis and qualities of these polymers are studied in polymer chemistry.
- Biophysical. Biophysical chemistry is a sub-discipline of biophysics. Thus, it brings together three major science branches (physics, biology, and chemistry) to investigate reactions and systems at a molecular level. It is also used to characterize and develop new techniques for studying molecules.
- Bioinorganic. A few examples of inorganic compounds are metals. Many metals are essential for organisms. The study of such metals and their roles in biological systems and reactions is bioinorganic chemistry.
- Environmental. The reactions and processes that occur in the environment are studied in environmental chemistry.
There may be more concentrations than mentioned above. It is also possible that newer ones will be developed in the future.
What Is A Chemist?
The extensive knowledge of chemistry and its branches and concentrations would not be possible without people dedicated to its study. You can help expand chemistry knowledge by becoming a chemist.
A chemist applies chemical principles and knowledge to conduct experiments, analyze results, develop products, prepare solutions, maintain laboratories, and more. They may actively contribute to the field's understanding by conducting research, and they may have specialties.
A chemist's specialties include quality control, forensics, research, medicinal, agrochemistry, environmental, nuclear, and more.
How To Become A Chemist
Becoming a chemist requires a lot of studying and understanding of chemical reactions, concepts, and processes.
Here's how you can become a chemist:
- Earn your undergraduate degree in chemistry.
- Gain experience through internships.
- If needed in your country, register for a license.
- Secure a job as a chemist.
- Pursue a specialty by taking graduate studies.
While working in chemistry-related jobs may not need a license, it may allow you to land higher positions, especially those that involve managing laboratories or teaching courses.
Final Thoughts
Chemistry is essential in understanding the different reactions and processes that occur within this world and affect life. It encompasses many aspects, leading to the establishment of sub-disciplines like organic chemistry. Individuals interested in this field may pursue it as a chemist.


