The worksheets work on identifying the different phases of mitosis visually as well as by description. We also look at the multiplying of body cells (mitosis) vs. the multiplying of sex cells (meiosis). This series of worksheets will begin by labelling and defining the function of all the phases of cell division. We will breakdown both mitosis and meiosis separately. We will also compare and contrast these cell regenerating processes. We will lead you on to performing your own lab investigation with these body cells. A fun thing to have students do is to slice an onion root tip super thinly and extract some cells to look at under a microscope. I find it easier to use green onions since they mostly have roots exposed. You can use regular white onions, but they are a little harder to see, unless you have the correct type of stain available for your slides. These worksheets are perfect to help students understand the differences and similarities between these two processes.
Print Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.
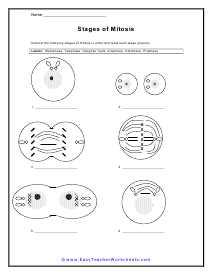
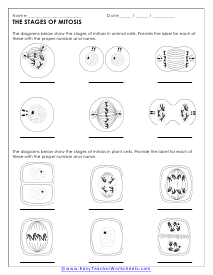
Stages of Cell Division
The diagrams below show the stages of cell division in animal cells. Provide the label for each of these phases with the proper number and name.
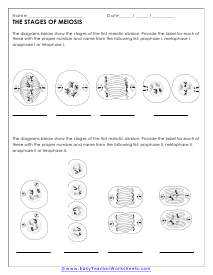
Stages of Meiosis
The diagrams below show the stages of the first meiotic division. Provide the label for each of these with the proper number and name of each stage.

Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
Place check marks in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the listed items apply to mitosis, meiosis or both.
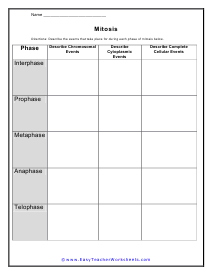
The Division of Body Cells
Describe the events that take place for during each phase of body cell division below.
What Is the Difference Between Mitosis and Meiosis?
The human body is an amazing thing; it contains trillions of cells which all replace themselves by dividing into two duplicates. Our bodies create slightly different sex cells to create eggs and sperm, each containing exactly half of our genetic information. But how exactly does this complicated process work?
Mitosis and meiosis are the two different types of cell division. Mitosis is the process used in most cells and results in two diploid (46 chromosome) daughters. Meiosis is used in the sex organs and results in four haploid (23 chromosome) sex cells.
Mitosis produces most of your body’s cells, your bones, organs, and muscles; meiosis only produces eggs in women and sperm in males. The primary difference between the two is how the chromosomes are separated and recombined, an essential part of human reproduction. Keep reading to learn more about how both of these processes work.
All body cells have a short life span. To make sure organisms can continue to survive, they constantly need to make new copies of them. To do this they undergo a process of duplicating themselves. There are five phases associated with this process. The first phase is named Prophase. This is where the cell duplicates its DNA. The second phase is called Metaphase this is where the DNA lines up in the middle of it. The third phase is where the chromosomes (DNA) begins to split and move itself into two cells. During the Telophase, it actually pinch off into two separate beings. The final stage is really when nothing is going on and that phase is called Interphase. I refer to it as the in between phase. This process of self-replication of body cells is called mitosis. If this process takes place in a sex cell (sperm or egg) it is called meiosis. In mitosis the division only occurs once which creates two cells from one. As a result, both new cells are identical copies of the original (parent). In meiosis the division occurs twice. So that single egg or sperm cell create four new cells that have only part of the original gametes genetic information. Therefore, sex cells are genetically diverse. This is also why the babies that sex cells form as genetic diverse too.
Mitosis, Meiosis, and Chromosomes
Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. The primary purpose of this is the duplication and recombination of chromosomes. Before mitosis or meiosis occurs, the cell duplicates its own DNA, a process called interphase.
In the first part of both mitosis and meiosis, the pairs of chromosomes line in the center of it. The chromosomes are pulled apart by microtubules during the first part of prophase. Prophase takes place in both meiosis and mitosis.
After prophase and metaphase, during which the chromosomes separate, the cells move into telophase, which ends the first stage of division. The purpose of cell division in both cases is the duplication and separation of the chromosomes, which is critical for genetic diversity.
What Is Mitosis?
During mitosis, the chromosomes are pulled apart, and a new cellular membrane forms between the two bundles. The chromosome bundles disassociate, and two new cells, which are identical to each other, have now formed.
Mitosis is essential for the health of cells. Your body’s cells have a limited life span and are replaced periodically. Fortunately, your body also makes new copies of them constantly to keep up with the demand. Mitosis also helps ensure genetic health in your cells by constantly replicating healthy cells faster than any flawed cells.
What Is Meiosis?
A slightly different process is used to create a new human being. Meiosis divides the chromosomes into four separate strands. After the first prophase, the chromosomes are carefully lined up so that all “homologous” or nearly identical chromosomes are aligned.
In the second prophase, the two homologous strands are separated so that there are now four identical strands of DNA. The cell divides and becomes four sex cells with 23 chromosomes.
The purpose of meiosis is to create these haploid, or 23-chromosome cells so that they can combine with other haploid cells and then combine into a 46-chromosome cell following fertilization. Combining DNA like this is how humans have maintained our genetic diversity over thousands of years.
Important Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
The primary difference between mitosis and meiosis is the second division and the final type of cells produced during meiosis. Meiosis is the specialized version of cell division intended to create unique DNA types.


