This collection of worksheets provides students with the opportunity to be introduced to algebraic fractions and how to solve them. Two complete sets of worksheets introduce your students to the concept of adding and subtracting algebraic fractions, provide examples, short practice sets, longer sets of questions, and quizzes. Fractions are difficult enough, why don't we just throw some algebra in there too? These worksheets will help your students learn how to solve problems involving algebraic and rational fractions. There is also an irrational version of algebraic fraction worksheets available on our Algebra page.
Print Algebraic Fraction Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.

Adding and Subtraction Algebraic Fractions Lesson
Follow the steps to solve the following problem: 2/4 – 2b/8. We walk you through the entire process in this lesson. You will then complete the practice problems. Example: 4n/4 – 4n/8

Add and Subtract Worksheet 1
Add and subtract the algebraic fractions. Example: 4a/2 – 2a/4. There are 10 problems like this to solve.

Worksheet 2
We spend a little more time concentrating on subtraction in these problems. There are plenty of addition operators.

Algebraic Fraction Review
It really helps if you start by finding the least common denominator (LCD) and then process the rest from there. This review sheet includes a completed problem and 6 review problems for you to work on.

Skill Quiz
Use this quiz to see if the skill has sunk in for students. This has ten problems and a scoring key. The answer key is readily available as well.
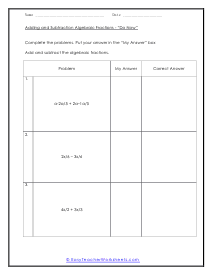
Do Now
Complete 3 problems dealing with algebraic fractions. Put your answers in the "My Answer" box and check to see if they are correct. We use common variables such as: 2x/6 – 3x/6

Operations within Rational Algebraic Fractions Lesson
This lesson setups the problems slightly different, but the underlying skill remains the same.

Operations with Algebraic Fractions Worksheet 1
Solve the following rational fractions. Remember to start with the LCM. Example: x/3 + x/9

Worksheet 2
We work on the same skill, but we step up the vales of the constants here. It does not make it much more difficult to solve.

Review Sheet
Practice this skill by solving the following 6 problems. This is a nice take home sheet to give out before a quiz.

Operations Quiz
Solve the following 10 algebraic fractions. This are a bit more complex. They all follow the example: x/(x + 8) + x/(x + 8) – 2
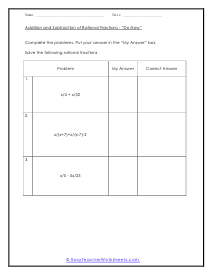
Do Now
Complete these 3 problems as a class. It is a nice way to introduce the topic. Example: x/4 + x/32

Multiplication and Division Lesson
Follow the steps to solve the following problem: (5x2/x – 2) (x2 – 4/10)
Complete the practice problems. Example: 4x2/(x - 3) [(x2 - 9)/16]

Multiplication and Division Worksheet 1
Multiply and divide these algebraic fractions to solve them in their simplest form. Example: 3x2/(3x-9) [(x2-9)/15]

Worksheet 2
Multiply and divide these algebraic fractions to solve for the variable that is present. Example: 5m/(5m+20) [(4m+16)/5m]

Review Sheet for Multiplication and Division
Practice this skill by completing the problems below. Here is an example of the problems that are present: 2a/(6a+6b) [(a+b)/2a2]
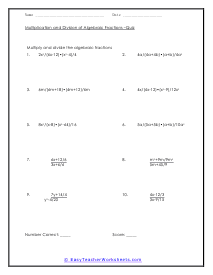
Skill Quiz
Your ability to multiply and divide are examined on this quiz. Example: 5a/(5a+5b) [(a+b)/10a]2
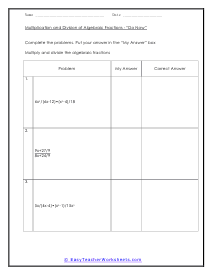
Complex Do Now Sheet
A class activity that you should do as a class as you approach higher levels with this skill. Example: 5x/(4x-4) [(x2-1)/15x3]
How to Solve Algebraic Fractions
Any fraction that uses a variable in the numerator or denominator is an algebraic fraction. In algebra, we do fractions the same way as in simple arithmetic. We can add, subtract, multiply and divide fractions.
These can be identified by simply looking for an unknown variable being present in the numerator or denominator of a fraction. Since fractions that have a denominator of zero are not possible, variables that are denominators can not exist where the denominator would equal zero. Some students latch on to this thought and think that the unknown value cannot be equal to zero. That is not the takeaway we want to leave students with. They can in some circumstances be equal to zero. What ever the overall operations result in cannot be equal to zero. In most cases we are just asked to reduce the fraction and not process it at all. You will find that having the ability to factor well comes in very handy with this topic. I highly encourage you to review factoring prior to attacking these types of problems.
For example, in the fraction y/4, the variable y makes the algebraic fraction. In an algebraic expression, the denominator has certain boundaries that are why it cannot be divided by zero.
In the fraction 4/(x-3), x cannot be equal to three (x≠3)
In the fraction 6/(b2a), neither a nor b can equal 0 (a≠0, b≠0)
Frequently, people find this process difficult, but with the right instruction, it can be straightforward. We will provide a step-by-step guide on completing these calculations and practice problems for you to try on your own. So let's get started!
Algebraic fractions are a pain for many students, but with the right approach, they can be conquered.
First, identify the algebraic fraction and what is being asked of you. Is it an addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division problem?
Second, understand what each term in the equation represents. In other words, what is the literal meaning of the equation?
Lastly, use the order of operations to solve the equation. This means first working with parentheses, then exponents, then division and multiplication (from left to right), and finally addition and subtraction (from left to right).
By following these steps, you can methodically work through any algebraic fraction problem.
What are Undefined Algebraic Fractions?
In the world of math there are a huge variety of numerical expressions. There are ones that contain just numbers, while there are more with variables. There are some containing only one variable, while others contain more than one variable. There are some that have denominators, and some are there without denominators.
The numbers that have denominators and variables are going to end up with an undefined point here.
Undefined means that at that particular point, there is no answer to that question. Sort of like a value where you have more questions than an answer. It occurs when the denominator is zero. This causes division to take place by zero. Since we cannot divide by 0, we end up with an expression that cannot be solved by us. We end up with more questions rather than getting an answer.
The division cannot be done by the number 0; hence the fraction can be termed as an undefined algebraic expression due to this:
1/x + 2
This expression is undefined when the x will equal to -2. We would state this as: x = -2
When you are talking about a fraction Nx/Dx, you can see the Nx is the numerator. The second one, or the Dx, is termed as the denominator and is written on the lower part. If the denominator is equal to zero, then the expression would be termed undefined.
This is due to the fact that division cannot be done when zero is placed as a denominator, and it therefore, leads to stating the expression as undefined.
Now that you may have an idea about how the denominator value can lead to the statement being undefined, we can proceed with an example, which will help in clarifying this a bit more.
You can get a basic idea about this undefined algebraic expression through this example.
EXAMPLE:
Here is an example of an undefined algebraic expression.
3a/(a2 - 4)
Now, we need to set the denominator. The denominator should be kept at the value of 0 for this undefined algebraic expression.
a2 - 4 = 0
a2 = 4
A = ±2
The domain would be: All the real numbers but not a = 2.
Neither is it a = -2
A: {a ≠ ±2}
This is an example that helps in understanding undefined algebraic expressions. Simply, zero as a denominator makes this an undefined algebraic expression.
The Zero Factor
0 is considered to be the integer that is placed just before the number 1. The zero is neither included in the positives nor in the negatives. 0 is an even number and also is considered a whole number. The value, as you must know, is nothing.
While 0 was used since the early times, the Greeks derived a symbol for it in 130 AD, and after that, it was used in almost all the calculations.
When you are dividing something, you are generally breaking them up into smaller parts. When it comes to zero, it is already the smallest number and has no value. Hence dividing it up would be problematic. Hence, the undefined algebraic expressions help in the solving of these problems.


