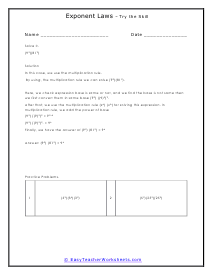
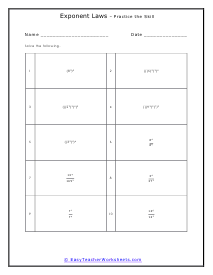
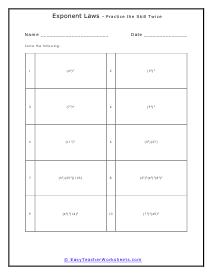
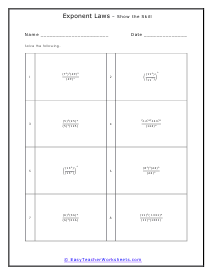
The law of exponents is a three-pronged set of standards that we apply to the use of exponents. An exponent is a value that raises a base to a power. The exponent just indicates how many times the number will be multiplied by itself. For example: in the value 93 (the base 9 is to be multiplied by itself 3 times.) It would just be a short form of writing 9 x 9 x 9. You will sometimes here exponents referred to as indices or powers. In addition to this there are two other considerations when using exponents. A negative exponent indicates an inverse operation with the exponents, instead of multiplying we would divide (with negative exponents present). A fractional exponent means for use to take the nth root of the value. We will apply all these parameters to the problems that we will manage below.
This cadre of worksheets looks at the common fundamentals of operations with bases that contain an exponent. When performing the product of exponents that contain the same base, just find the sum of the exponents. When you are taking the quotient of exponents with the same base, just find the difference between the exponents. When you have a negative exponent, you can make it positive by finding the reciprocal of the base. Below you will find worksheets that give your students practice in dividing and multiplying equations that contain exponential numbers. Please note that answers will contain exponents and will not be whole numbers. These worksheets explain how to solve problems by using several of the laws of exponents. These are usually helpful for narrowing down operations between the values.