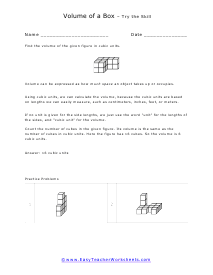
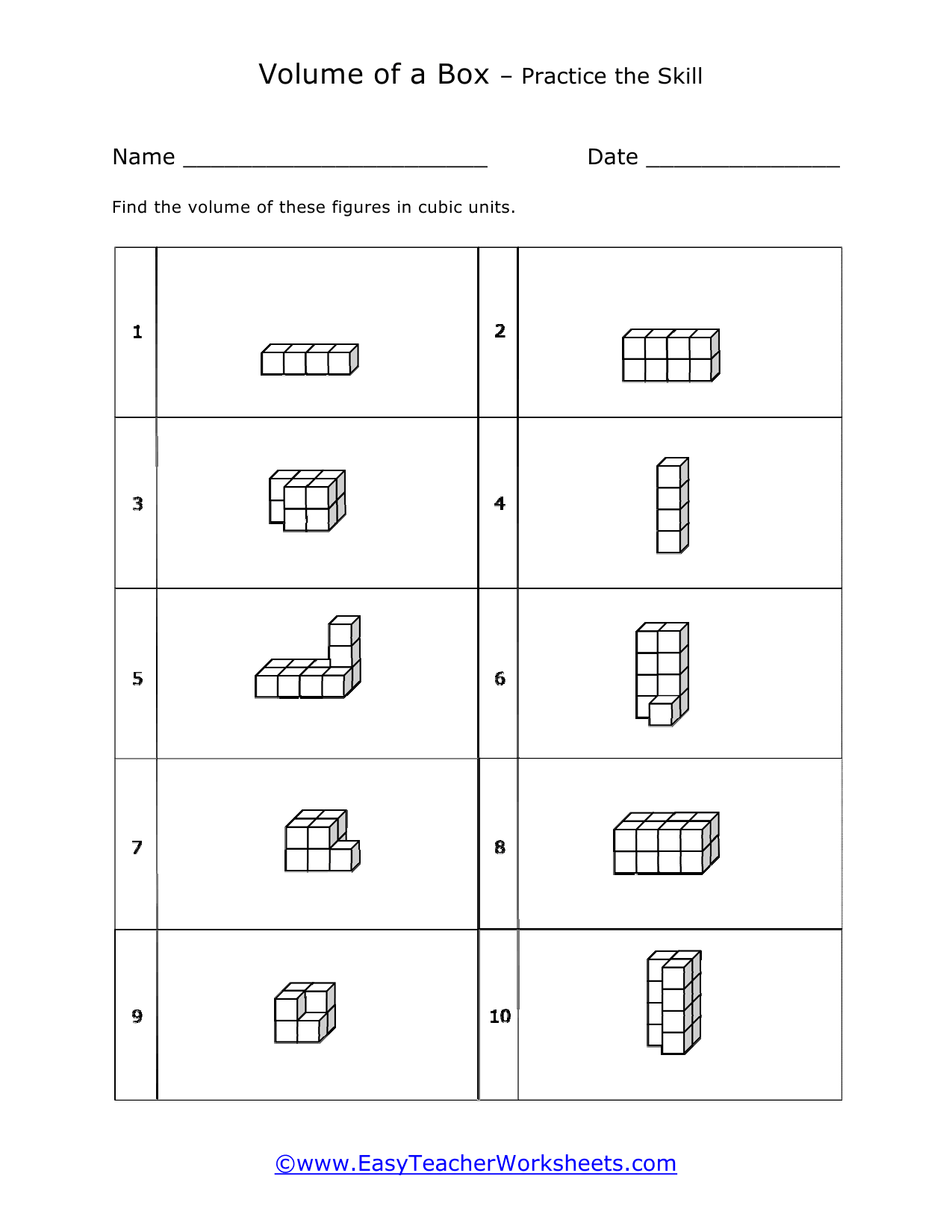
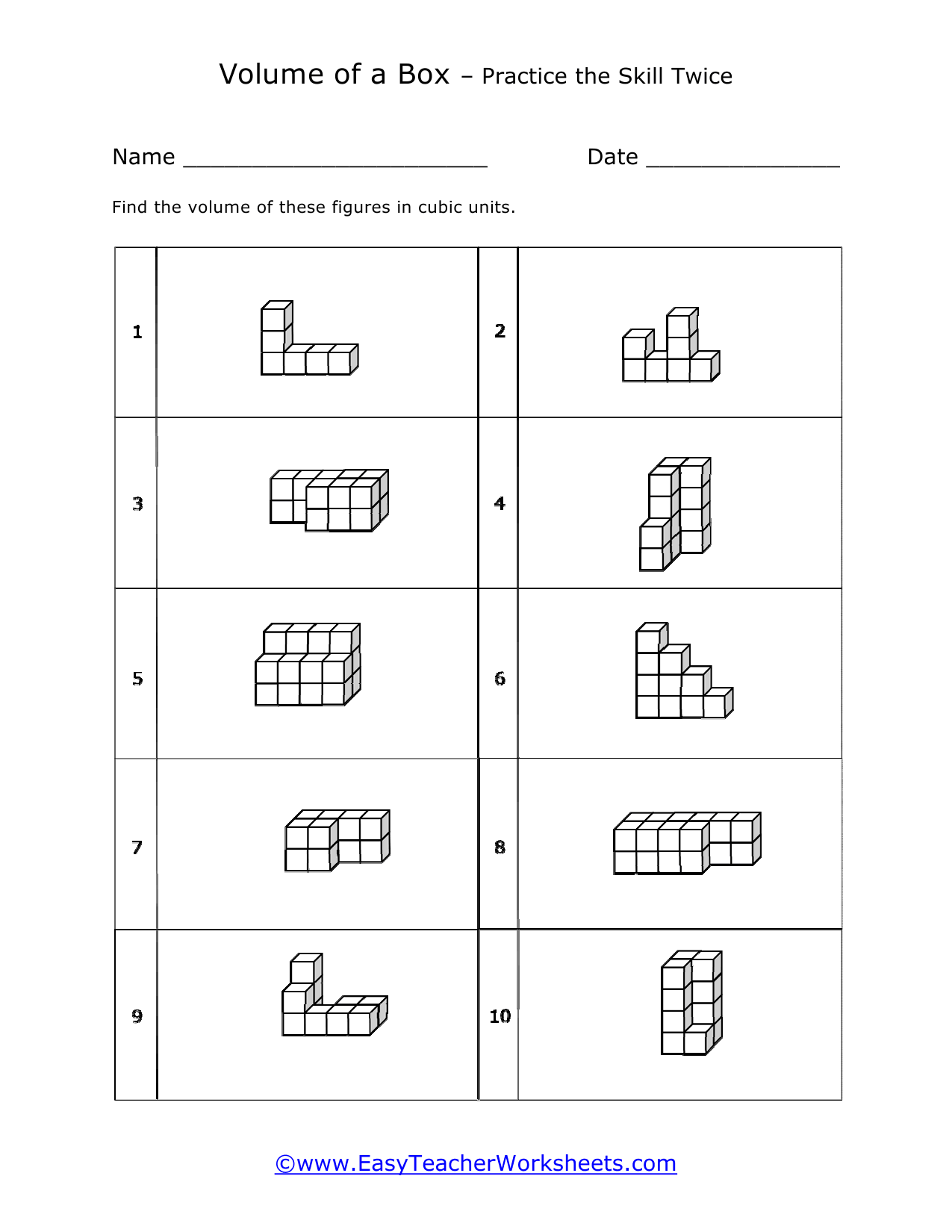
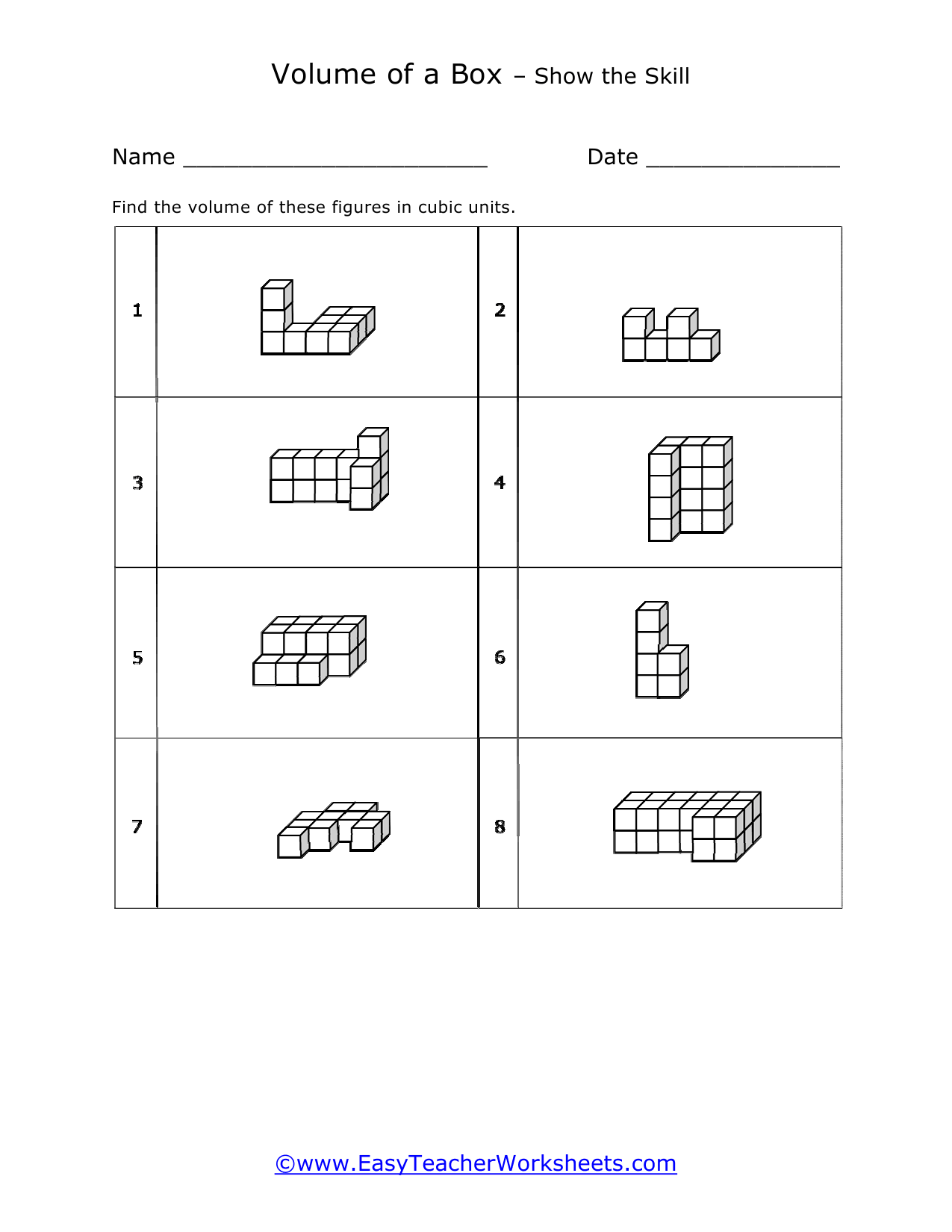
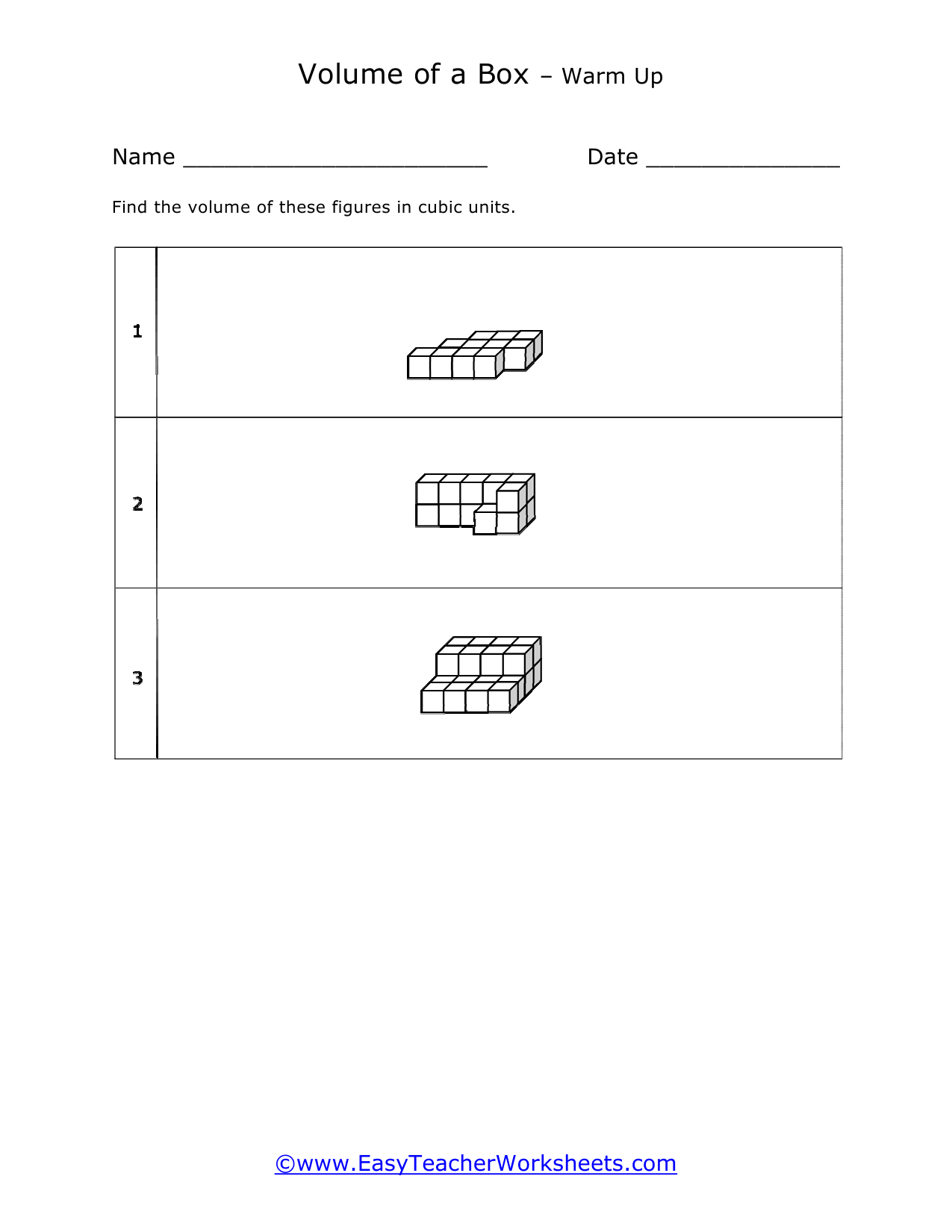
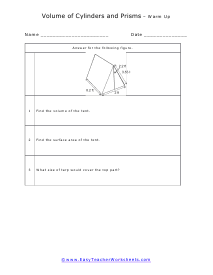
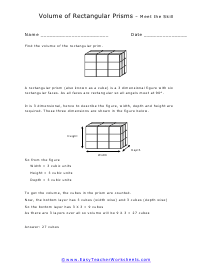
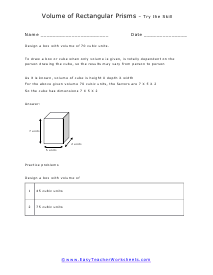
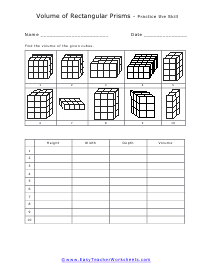
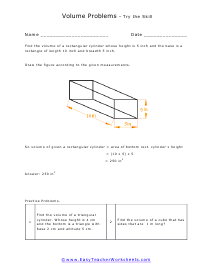
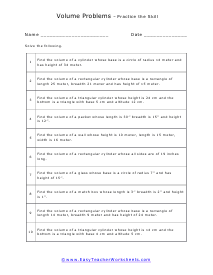
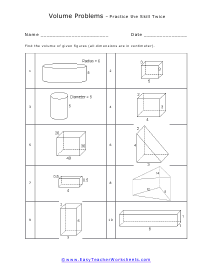
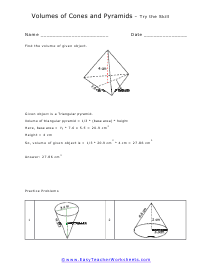
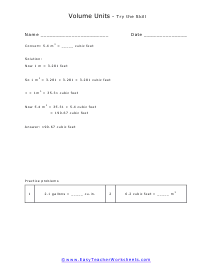
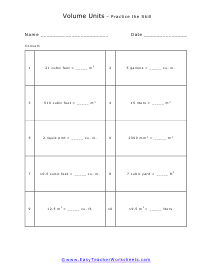
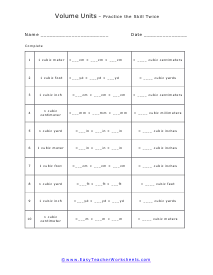
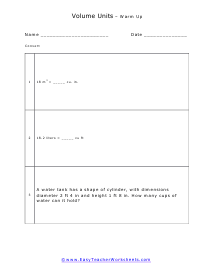
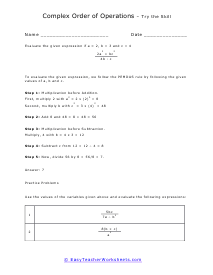
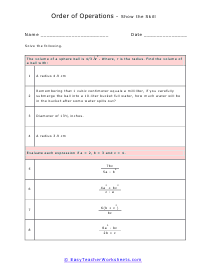
Volume is a measure of how much space something takes up. It measures the capacity of a given object. Every measuring system that exists in the world has defined a unit volume for that system. To put it simply, the volume can be defined as the extension of the concept of area. But in reality, it goes beyond this. When someone refers to the volume of an object in that system, what they mean is how many times that unit volume is contained within the object. For example, they say that the volume of a glass filled with water is 35.6 cubic inches. This means that the glass of water can hold up to 35.6 cubic inches of water in it. The units used for measuring the volume depends on a range of factors, in which one very obvious is, the system it is being measured in. For example, In the British system, a volume may be measured in barrels, bushels, pecks, tea, and tablespoons, as well as many other units. These units may have more than one meaning since they are different. For example, the size of the barrel can differ and can range anywhere from 31 to 42 gallons. However, the standard units used in this system are the cubic inch or cubic foot and the gallon.
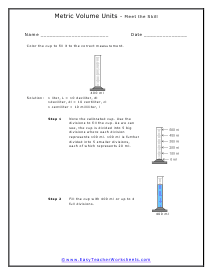
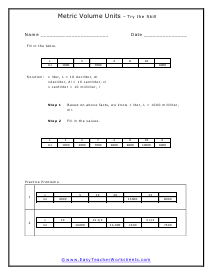
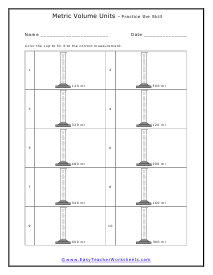
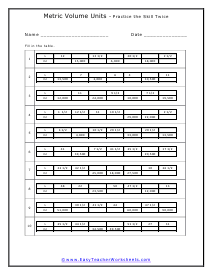
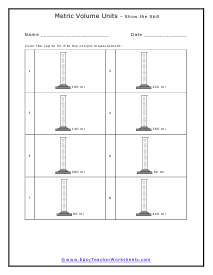
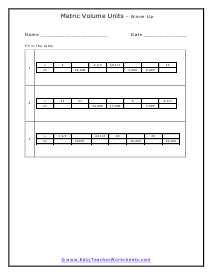
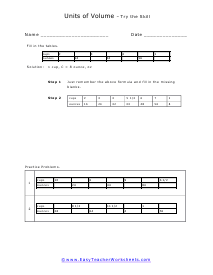
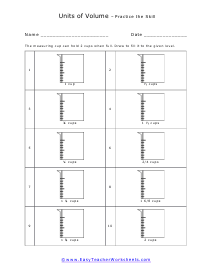
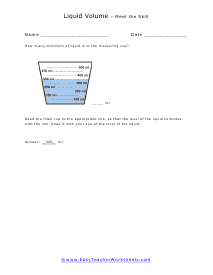
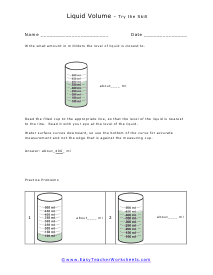
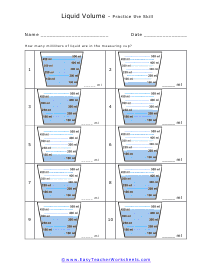
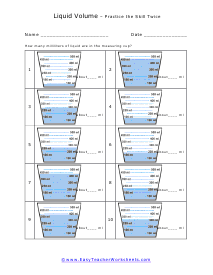
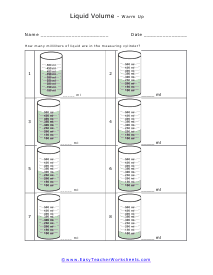
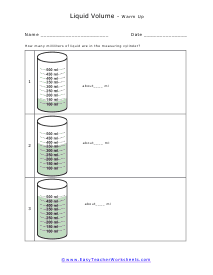
You can also measure the volume of sound, but this very subjective. What is considered loud to one person is not to another. What is the old (pun intended) "If it is too loud, you are too old!" In this section we focus on calculating the liquid and solid volume. The volume of a solid is usually expressed in cubic centimeters. The volume of liquids is usually express in relation to liters. These worksheets explain how to do read and calculate units of volume. Students will complete equivalency charts, fill in graduated cylinders, perform complex order of operations, and other activities.