How to Borrow From Other Place Values in Large Digit Subtraction Problems - Do you the concept of carrying in addition problems in mathematics, where you put/add an extra value to the number to balance the answer? Borrowing or regrouping in subtraction is just the opposite of this idea. In subtraction, you borrow value from the next biggest digit in the left column to support the digit, which is smaller in value and get an answer for that digit. Some of you might hear the term regrouping. Nevertheless, borrowing and regrouping are the same. The extra amount that you take from the left column is known as the borrowed amount or digit. For example; 4 - 2 = 2 (this required no borrowing or regrouping) 36 - 9 = 27 (this required borrowing or regrouping from the digit 3) The borrowing or regrouping can also move to the next two or three digits in line. For instance, in this example, 624 - 7 = 617, we got this answer by borrowing value from 6 rather than 2. Therefore, it is not certain where the borrowed value lies.
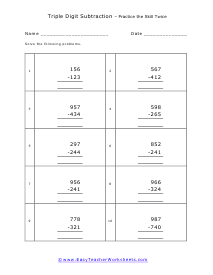
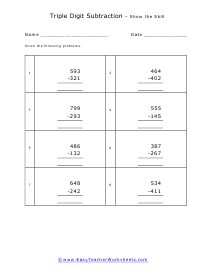
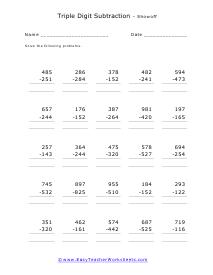
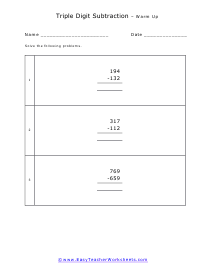
These worksheets are for the students who already have proficiency subtracting single and double digits from single, double, and triple digits. They will develop their subtraction skills by learning to subtract triple digits from triple digits. Students should already have an understanding of mathematical place value terms. Students should already have a firm understanding of and ability to use the technique of borrowing to solve subtraction problems. Your students will use these worksheets to learn how to solve more complex subtraction problems. This set of worksheets contains step-by-step solutions to sample problems, many simple practice problems, a review, and a quiz. When finished with this set of worksheets, students will have demonstrated skill in subtracting triple digits from triple digits. These worksheets explain how subtract triple-digit numbers from triple-digit numbers. Sample problems are solved and practice problems are provided.