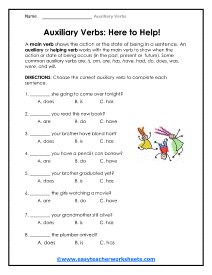
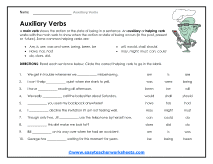
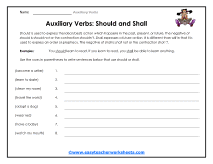
Every sentence that you read will have a verb to describe an action (action verbs) or condition (linking verb) describe within it. These actions or conditions can take place once or over time. Writers will also include a secondary verb in some situations to add a nuance to a sentence. The secondary verb can be used to express a tense, give a voice, form a negative or a question. These secondary verbs are called helping or auxiliary verbs. The most common forms of these verbs are be, do, have, and is. These words often attach themselves to the main verb within the sentence. They are also the most common verb form found in the English language. One simple way to identify these verbs is to look for verbs that express a tense, that is a dead giveaway. A distinction of a modal auxiliary verb is that they never change form which means that they will not -ed, -ing, or -s endings. This is because they only have one form. This would include words such as: can, could, shall, should, will, and would. Modal auxiliaries express a sense of obligation, indicating that something must be done.
These worksheets will help students learn to identify and properly use these verb forms in sentences. The worksheets below help students learn how to use these words properly in sentences. We work on the grammar, mechanics, and syntax issues that arise often in the English language. You will be advance on to writing full paragraphs that demand the use of these types of words. This leads us to correct tenses within what we write. Students will be made aware of how a single word change can have a major impact on the message that comes across to readers.