Pronouns are words that take the place of a noun. Like nouns, pronouns can be singular, plural, or possessive. They can also be subjects or objects. The proper use of pronouns breathes life into our language. It helps us to avoid constant repetition and makes sentences easier to comprehend. The five most common pronouns used in the English language are: he, she, it, they, and this. The following collection of worksheets will help your students learn about pronouns. Activities include replacing selected words in a given sentence with the corrected word, identifying the antecedent a selected word might refer to, classifying selected words as objects or subjects, rewriting sentences to include a fixed word form, and more. Take these shortened proper nouns to the next level with these worksheets. Earn credit for each identification and replacement exercise. I find those to be the most difficult for most students.
Print Pronoun Worksheets
Click the buttons to print each worksheet and associated answer key.

Underline It
Rewrite each sentence below, replacing the underlined nouns with a more proper form of the word.

Pronouns and Antecedents
In each sentence, identify the antecedent of the bolded word. Write it on the line.

Subjects and Objects
Write S on the line if the underlined word is subject based. Write O on the line if it is a object based.

Using Pronouns
Rewrite the second sentence in each pair, using a more specific word to give it more meaning. You can begin to see how mastering this portion of grammar can elevate the language that you will use.
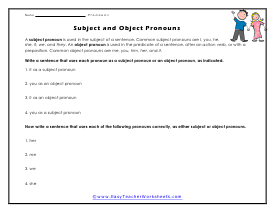
More Subjects and Objects
Write a sentence that uses each pronoun as a subject or an object, as indicated. Now write a sentence that uses each of the following word forms correctly, as either a subject or an object.

Identifying Their Antecedents
These guys first steal the words whole meaning and then it goes as far as trying to bury them in the sentences.
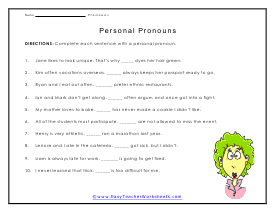
Personal Word Usage
Complete each sentence with a corrected word form. You will come up with the vocabulary word all by yourself.

Using Pronouns Correctly
Underline the error in each sentence. Write the correct word on the line. Then use each of the following words in a sentence.
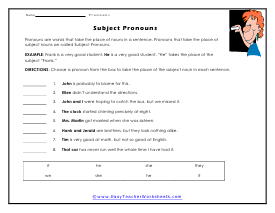
Subject Word Forms
Choose a word from the box to take the place of the subject word in each sentence.
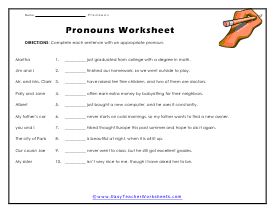
Appropriate Pronouns
Use the left column to properly complete the sentences on the right side of the paper.

I Told You Before: Subject and Object
Is the missing word in each sentence being used as a subject or an object? Write the correct word on the line.

Placing the Right One
What is the correct usage? Is something wrong here? Write the corrected word on the line.

Identification Work
First find the word and then jump in a new word for the best use of the writing purpose.

2 Tasks For You
Rewrite each sentence below, replacing the underlined nouns with a pronoun. Then determine if that word is being used as a subject or an object? Finish by writing that corrected word in there.

Writing with Personal Nouns
Rewrite the second sentence in each set, replacing the subject with crazy other words.
Working with Pronouns
What Are They?
To understand pronouns better, let us recall what nouns are. Nouns are names of things, places, or people.
Example: Disneyland (place), Albert Einstein (name), my bedroom (place)
A pronoun is a word you use in place of a noun when your reader or listener is already familiar with the specific nouns you're talking about.
Pronouns: I, me, he, she, they, that, it, someone, everybody, whose, whoever, et cetera.
Let us see some examples of pronouns to understand them better.
Example: I have a book. It's new.
Here "it" is a pronoun since it is used to describe the already mentioned object, which is "a book."
Example: That is my dog. It is black and white.
Here "He" is the term of interest here.
There are seven common forms of pronouns you will use in your writing. Personal pronouns are used to specific a particular person or thing. Their form can change to indicate a number, gender, or case. The demonstrative form is used to point to something specific within a sentence. They often are used to indicate items in space or time. The interrogative form is used to as questions. Words such as: what, which, and who/whom fall into this category. The relative form is used to link a phrase or clause to one another that was mentioned previously in your work. The indefinite form is used to refer to a person or thing without being specific. The most common word forms for this are: all, anyone, each, everybody, and someone. The reflexive form is used to refer back to the subject of the sentence or clause. Example words of the reflexive form include: myself, herself, himself, and ourselves. The intensive form is used to add a higher level of emphasize on the antecedents of the sentence. This is a more complex form than we expect for writers at this level.
Antecedents
When we use a pronoun, the first rule is introducing a noun before it. Introducing a noun before makes it easier for the person to understand the sentence better. The introduced nouns are called antecedents.
Examples: My teacher gives us extra work, and I still appreciate her.
"My teacher" here is an antecedent since it is the noun used before the pronoun "her" to make the sentence easier for us to understand.
Example: The board is too far away for Amy to read it.
"The board" here is an antecedent, and "it" is a pronoun.
We don't need antecedents for pronouns like I, we, me, you, and us. This is because the listener or reader already knows what you are discussing. An antecedent may be used according to given circumstances.
Let us discuss some different types of pronouns to grasp them better.
Personal Forms
The term "personal pronoun" refers to any pronoun that can refer to a particular person or group.
Examples: She, her, I, me, we, us, he, him, etc.
Here are some examples of personal pronouns.
Example: David is late for class today. He will have to come up with a good excuse.
"he" is a personal pronoun here.
Example: Ronnie is leaving today. She is moving to Australia.
"She" is a personal pronoun.
Relative Forms
Relative pronouns are another sort of pronoun. They serve as an intermediary between independent and relative clauses. In most cases, they serve to clarify more about the sentence's subject.
Examples: what, that, which, who, whom
Usually, "who" is used to talk about people, while "which" and "that" is used to talk about animals or things. Here are some examples of relative pronouns.
Example: My aunt who lives in England will visit us today.
Here "who" is a relative pronoun.
Example: All the animals that were rescued today are fine now.
Here "that" is a relative pronoun.
Possessive Forms
Pronouns that show possession are called possessive pronouns.
Examples: my, our, his, her, their, its
Possessive pronouns can be called possessive adjectives when they modify a noun in a sentence. Let's look at some examples of possessive pronouns in sentences.
Example: Your bag looks new.
"Your" is a possessive pronoun.
Example: Our house is at the end of the street.
"Our" is term in this sentence.
Example: My cat is scared of new people.
"My" is the word that fits this profile.
Other types of pronouns and their examples are:
Demonstrative Forms
Demonstrative pronouns point to a specific object or concept in a sentence. Singular or plural, these pronouns can refer to anything in space or time.
Examples: That, this, these, those
Indefinite Forms
A pronoun that lacks a distinct, familiar referent is indefinite. Differences exist between indefinite and definite pronouns. Indefinite pronouns can indicate both countable and uncountable nouns.
Examples: One, nobody, both, everybody, both
Reflexive Forms
When the subject and direct object are identical, a reflexive pronoun can function as the direct object in a sentence.
Examples: myself, yourself, oneself, ourselves, himself
Intensive Forms
The functions of intense and reflexive pronouns are nearly the same, although they serve different purposes. An antecedent or subject can be emphasized by using intensive pronouns.
Examples: ourselves, myself, himself, oneself, itself, yourself
Interrogative Forms
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions about people or objects
Examples: who, which, what, whose
Reciprocal Forms
A pair of reciprocal pronouns describes a situation in which someone or something does something to another and receives the same thing in return.
Examples: one another, each other
Distributive Forms
When more than one person or thing is present, a distributive pronoun indicates that each person or thing is taken separately.
Examples: any, either, neither each
Conclusion:
Pronouns are essential in English grammar; they are used in almost every sentence. We hope this article helps you understand pronouns better.



